Is there a difference between fiberboard and chipboard, and which is better?
Due to the steady decline in the stock of industrial timber, the production of various materials made from sawmill and wood processing waste is becoming more relevant than ever. It is to this group that fiberboard and chipboard belong, without the use of which neither the furniture industry, nor construction, nor many other industries (machine and shipbuilding, container production, etc.) can do.
Consumers often confuse these materials, although their production, appearance, and functional properties differ. What is the difference?
Production
Chipboard, as the name implies, is created on the basis of a large fraction of wood chips. The source of raw materials for production is substandard wood, wood chips and sawdust.
The production process proceeds as follows: crushed raw materials are dried and wetted through nozzles with binders. Synthetic carbamide, phenolic or urea-melamine resins are used as a binder.
When using the latter in combination with paraffin emulsions, a moisture-resistant chipboard is obtained, which on the cut is distinguished by the presence of specific inclusions of greenish conglomerates. It is this material that is best used for finishing work and flooring in rooms with high humidity.

The processed mixture of chips and resins can be molded:
- single-layer, when chips of various fractions are mixed and evenly distributed over the entire plate;
- from two layers, when the underlying layer is made from waste, and the front layer is a mixture of thin and wide chips specially sorted on a separator;
- from two front layers made of selected raw materials and a core in which less quality waste is used.
The molded particle carpet is sent for pressing, drying, cutting the boards to size and grinding the ends.
As a finish, especially if chipboard is planned to be sent for decorative cladding in the future, grinding of the entire surface can be additionally applied.
Unlike particle board, wood fiber materials require, after splitting the raw material into chips, two additional stages of mechanical processing:
- initial coarse grinding on defibrators;
- finer grinding in refiners.
As a result, the wood is separated into individual fibers. Such macro-processed pulp is the basis of hardboard, and hemp fire, linen production waste, and waste paper can also be used in its creation. The mass composed according to the recipe is sent for further processing to tanks, in which it is soaked in a water mixture of hardening additives and glued with water-repellent substances.
 Fiberboard is the back walls of furniture, material for finishing the floor, camp and ceiling of houses and outbuildings
Fiberboard is the back walls of furniture, material for finishing the floor, camp and ceiling of houses and outbuildings The mixture prepared in this way enters the casting machines, after which it passes the stage of thermal pressing at a temperature of 210-230°C and a maintained pressure of 3-5 MPa.
The formed webs can additionally undergo thermochemical hardening, it is this effect that provides them with hard and superhard properties that are best suited for making structural elements of buildings, arranging a subfloor, and creating internal partitions.
Appearance
Quite large particles of wood are visually visible on the surface of unfinished particle boards, in contrast to them, hardboard resembles thick cardboard. A significant difference in the thickness of the material:
- Chipboard can be produced in sheets of at least 10 mm thick, and the maximum value of this value reaches 50 mm;
- Fiberboard is much more "elegant" - from 2.5 to 7 mm.
To improve the decorative properties, the surface of fiberboard and chipboard is often finished. But if hardboard is mainly painted as a finish, and technological methods of caching and lamination are used less frequently, then chipboard ennobled with melamine films is found everywhere.

The well-known floor covering, colloquially called "laminate", is essentially a floor covering made of high-density chipboard and lined with acrylic or melamine resin.
In addition, veneering can be used to finish chipboard panels - gluing veneer (the thinnest sheets of natural wood) onto the chipboard surface. It is veneered chipboard that is used in the manufacture of furniture.
Security
Evaporation of phenol-formaldehyde resin used to create chipboards is by no means harmless to human health. However, manufacturers are constantly working to improve the safety of their products, and urea, which is less toxic, is increasingly replacing formaldehyde. The best from this point of view are particle boards produced in Germany and Austria.
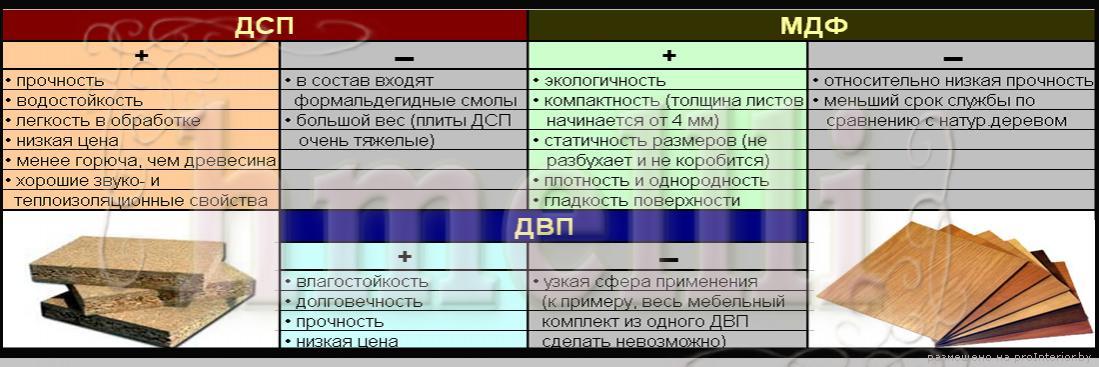
Ecologists have much fewer complaints about fiberboard, but before choosing a material, it is still better to ask the seller about the availability of a hygienic certificate of conformity. It should be remembered that products labeled with the letter E1 are more environmentally friendly, although their price is somewhat more expensive.
What material is better?
This question is somewhat incorrect, since in fact it is like comparing warm with soft. Each type of material is best used for its own purposes.
Chipboard is great for:
- implementation of interior partitions;
- wall insulation from the inside;
- arrangement of the subfloor;
- furniture production.
In the latter case, hardboard is also useful, because the back walls of cabinets and all kinds of drawers are made from this material. All kinds of wall surfaces are finished with fibreboard, especially in country houses, on balconies and in garages, because they are much less afraid of moisture than thick particle boards. Hardboard is also suitable as a substrate for the floor or an insulating layer on the ceiling, and real virtuosos of the construction industry can easily turn its sheets into an elegant interior arch or a patterned door.
