Specifications for technical entrance doors. How to install a door block? General requirements for the installation of products
EURASIAN COUNCIL FOR STANDARDIZATION, METROLOGY AND CERTIFICATION
(EASC)
EURO-AZIAN COUNCIL FOR STANDARDIZATION, METROLOGY AND CERTIFICATION
(EASC)
INTERSTATE STANDARD GOST
31173-2003
STEEL DOOR BLOCKS
Specifications
INTERSTATE SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNICAL COMMISSION
ON STANDARDIZATION, TECHNICAL REGULATION
AND CERTIFICATIONS IN CONSTRUCTION (MNTKS)
Moscow
General requirements for the installation of products
Although painting steel door is an easy project For most homeowners, there are several considerations that can make a big difference in the durability of a finish and the need for early repairs. Painting a steel door should not be done for 8-10 years if done properly.
While the front door is a great place to make a dramatic statement, a dark or red color will need to be repainted much sooner. Steel doors can become quite hot when exposed to direct sunlight. More light colors with a touch Brown will last longer when exposed to direct sun rays. Storm doors can act as a greenhouse. Heat trapping and premature paint. Try to leave the top window of the storm door open to vent that heat. 100% acrylic paints will use traditional oil paints when used on a steel door. High quality outer acrylic paint for the home is more resistant to sunlight. Before installation, seal the pin strip with a small ball. This will act as a gasket and keep moisture from collecting behind the plate. Moisture will cause the paint to fail and the steel to rust.
- The color you choose will affect how long the paint lasts.
- Dark colors will disappear sooner.
- Exposure to the sun will also cause the finish to fade.
Foreword
The Eurasian Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (EASC) is a regional association of national standardization bodies of the states that are members of the Commonwealth of Independent States. In the future, it is possible that national bodies for standardization of other states will join the EASC
The EASC has an Interstate Scientific and Technical Commission for Standardization, Technical Regulation and Certification in Construction (MNTKS), which has the right to adopt international state standards in the field of construction
The goals, basic principles and basic procedure for carrying out work on interstate standardization are established by GOST 1.0-92 “Interstate standardization system. Basic provisions” and MSN 1.01-01-96 “System of interstate normative documents in construction. Basic Provisions»
About the standard
1 DEVELOPED by the Window and door technology and FSUE Central Design and Technological Bureau (FSUE TsPKTB of Gosstroy of Russia) with the participation of ANEO Academy "Safety and Law" and the firm "Abloi Oy", Bjerkboda plant, Finland
2 INTRODUCED by Gosstroy of Russia
3 ADOPTED by the Interstate Scientific and Technical Commission for Standardization, Technical Regulation and Certification in Construction (ISTCS) on May 14, 2003
Voted to accept:
Short name of the country according to MK (ISO 3166) 004-97 Country code according to MK (ISO 3166) 004-97 Abbreviated name of the public administration body for construction
Armenia AM Ministry of Urban Development of the Republic of Armenia
Kazakhstan KZ Kazstroykomitet of the Republic of Kazakhstan
Kyrgyzstan KG State Commission for Architecture and Construction under the Government of the Kyrgyz Republic
Moldova MD Ministry of Ecology, Construction and Territorial Development of the Republic of Moldova
Russian Federation RU Gosstroy of Russia
Tajikistan TJ Komarchstroy of the Republic of Tajikistan
Uzbekistan UZ Gosarchitektstroy of the Republic of Uzbekistan
4 INTRODUCED FOR THE FIRST TIME
5 Entered into force on March 1, 2004 as a state standard Russian Federation Decree of the Gosstroy of Russia dated June 20, 2003 No. 76
Information about the entry into force (termination) of this standard and changes to it in the territory of the above states is published in the indexes of national (state) standards published in these states.
Information about changes to this standard is published in the index (catalogue) " Interstate standards", and the text of the changes - in the information signs "Interstate standards". In case of revision or cancellation of this standard, the relevant information will be published in the information index "Interstate Standards".
Most available on the market are galvanized steel. Others are made of aluminum panels or fully glazed aluminum profiles. They are 1 to 2 inches thick, with or without insulation. Here is some basic information to help you!
One, two or three layers: what does it mean?
Manufactured from a single sheet of molded steel and typically 2 inches thick to give a certain degree of strength to the panel structure. Garage door manufacturers offer an extra styrofoam panel covered with a hard styrene sheet to prevent insulation from leaking.
Polystyrene or polyurethane: which is better
- These Garage Doors made of steel sheets with insulation between them.
- The insulation is usually made of expanded polystyrene or polyurethane.
- Styrofoam insulated doors are 1, 1¾ or 2 thick.
- Polyurethane insulated doors are 1" to 2" thick.
- The vast majority of these doors are 1 or 1¾ thick.
Content
1 area of use
2 Normative references
3 Terms and definitions
5 Technical requirements
5.1 General provisions and design requirements
5.2 Dimensions and tolerance limits
5.3 Characteristics
5.4 Requirements for materials and components (including gaskets)
5.5 Requirements for hinges, locks and other locking devices
5.6 Requirements for product finishing
5.7 Completeness and marking
6 Acceptance rules
7 Control methods
8 Packaging, transport and storage
9 Manufacturer's warranties
Annex A (mandatory) Terms and definitions
Appendix B (informative) Examples of designs of product units and variants of drawings door panels
Annex B (normative) Requirements for security door units
Annex D (informative) An example of determining the strength class of a door unit
Appendix E (recommended) An example of filling out a passport for a door unit
Annex E (recommended) General requirements to the installation of products
Annex G (informative) Information about the developers of the standard
Are there other factors that may influence my decision?
First of all, let's define two types of insulation. Commonly known as Styrofoam, it is used to make coffee cups and protective packaging material for appliances and other goods. It expands: Heat is used to expand tiny Styrofoam beads into a precise shape. This is chemical composition of several products once mixed can swell to fill almost any space. Polyurethane is found in all sorts of different things: foam is used to make chairs and even car bumpers. Since garage doors vary from 8' to 18', insulation of the correct density must be found to ensure the correct heat resistance factor and ideal panel structural rigidity. It is also used in 1¾" thick front doors.
- Once the block is removed from the mold, it is cut into the required size and shape.
- In terms of insulation, it is less effective than polyurethane.
- Inch-inch, polyurethane is twice as effective as polystyrene.
- This mixture forms closed cells which give it high heat resistance.
- It's all about the density of the foam.
- The higher the density, the stiffer the insulation.
INTERSTATE STANDARD
STEEL DOOR BLOCKS
Specifications
Steel doors Specifications
Date of introduction - 2004-03-01
1 area of use
This standard applies to steel door blocks with installed locking devices (hereinafter referred to as door blocks or products) for buildings and structures for various purposes.
The standard does not apply to door units for special purposes in terms of additional requirements to fire safety, explosion and bullet resistance, exposure to aggressive environments, etc., as well as to the door blocks of protective cabins according to the current normative documentation.
The scope of specific types of products is established depending on the operating conditions in accordance with the current building codes and rules, taking into account the requirements of this standard.
The standard can be applied for certification purposes.
2 Normative references
This document makes reference to the following standards:
GOST 9.032-74 ESZKS. Paint coatings. Groups. Technical requirements and designations
GOST 9.301-86 ESZKS. Metallic and non-metallic inorganic coatings. General requirements
GOST 9.303-84 ESZKS. Metallic and non-metallic inorganic coatings. General selection requirements
GOST 9.401-91 ESZKS. Paint coatings. General requirements and accelerated test methods for resistance to climatic factors
GOST 9.402-80 ESZKS. Paint coatings. Preparation of metal surfaces before painting
GOST 99-96 Rotary cut veneer. Specifications
GOST 166-89 Calipers. Specifications
GOST 380-94 Carbon steel of ordinary quality. Stamps
GOST 427-75 Measuring metal rulers. Specifications
GOST 538-2001 Lock and hardware products. General specifications
GOST 1050-88 Rolled section calibrated, with a special surface finish from quality carbon structural steel. General specifications
GOST 2140-81 Visible defects of wood. Classification, terms and definitions, methods of measurement
GOST 2977-82 Sliced veneer. Specifications
GOST 4598-86 Wood fiber boards. Specifications
GOST 5089-2003 Locks and latches for doors. Specifications
GOST 5264-80 Manual arc welding. Connections are welded. Main types, structural elements and dimensions
GOST 5632-72 High-alloy steels and corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant alloys. Stamps
GOST 7016-82 Wood products and wood materials. Surface Roughness Options
GOST 7502-98 Metal measuring tapes. Specifications
GOST 8026-92 Calibration rulers. Specifications
GOST 8242-88 Profile parts made of wood and wood materials for construction. Specifications
GOST 8713-79 Submerged arc welding. Connections are welded. Main types, structural elements and dimensions
GOST 9416-83 Building levels. Specifications
GOST 10354-82 Polyethylene film. Specifications
GOST 11533-75 Automatic and semi-automatic submerged arc welding. Connections are welded at acute and obtuse angles. Main types, structural elements and dimensions
GOST 11534-75 Manual arc welding. Connections are welded at acute and obtuse angles. Main types, structural elements and dimensions
GOST 14771-76 Shielded arc welding. Connections are welded. Main types, structural elements and dimensions
GOST 15140-78 Paintwork materials. Methods for determining adhesion
GOST 21778-81 Accuracy assurance system geometric parameters in construction. Key points
GOST 21779-82 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Technological approvals
GOST 21780-83 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Accuracy calculation
GOST 23118-99 Steel building structures. General specifications
GOST 23518-79 Shielded arc welding. Connections are welded at acute and obtuse angles. Main types, structural elements and dimensions
GOST 25347-82 Basic norms of interchangeability. ESDP. Tolerance fields and recommended landings
GOST 26433.0-85 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Rules for performing measurements. General provisions
GOST 26433.1-89 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Rules for performing measurements. Prefabricated elements
GOST 26602.1-99 Window and door blocks. Methods for determining the resistance to heat transfer
GOST 26602.2-99 Window and door blocks. Methods for determining air and water permeability
GOST 26602.3-99 Window and door blocks. Method for determining sound insulation
GOST 30778-2001 Gaskets sealing from elastomeric materials for window and door blocks. Specifications
GOST 30971-2002 Mounting seams for adjoining window blocks to wall openings. General specifications
GOST 30972-2002 Glued wooden blanks and parts for window and door blocks. Specifications
3 Terms and definitions
Terms and definitions used in this standard are given in Annex A.
4 Classification and symbol
4.1 Products are classified according to the following criteria:
appointment;
design options;
type of finish;
performance indicators;
mechanical characteristics;
protective properties.
4.1.1 By purpose, door blocks are divided into:
outdoor (entrances to buildings, premises, as well as vestibules);
internal (entrance to the apartment and others intended for operation inside the building).
4.1.2 According to the design options, door blocks are divided into:
box design:
with a closed box;
with U-shaped box;
with a U-shaped box with an additional threshold;
by the number of canvases (including non-opening ones), direction and type of opening:
single-field (left and right opening);
double-sided (including with canvases of different widths);
with non-opening horizontal or vertical inserts;
with opening inside the room;
with outward opening;
according to the number of sealing circuits in the porch:
with one circuit;
with two or more circuits.
4.1.3 According to the type of finish, door blocks are divided into:
painted with paint and varnish and powder materials;
lined with leather (artificial or natural) and insulation;
pasted over with decorative film materials;
lined with wood or wood-based materials (including those with natural or synthetic veneer);
finished with glass (mirror) materials;
trimmed with decorative metal cladding;
combined (including from other materials).
Note - By agreement with the customer, it is allowed to use other types of finishes.
4.2 In terms of performance, door blocks are classified according to the reduced resistance to heat transfer, air and water permeability, and sound insulation.
4.2.1 In terms of the reduced resistance to heat transfer of the door leaf, the door blocks are divided into classes:
1 - with reduced heat transfer resistance of 1.0 m2 °C/W and more;
2 - with reduced resistance to heat transfer from 0.70 to 0.99 m2 °C / W;
3 - with reduced resistance to heat transfer 0.40 - 0.69m2 °C / W.
Note - Door blocks with a reduced heat transfer resistance of less than 0.40 m2 ° C / W are not subject to classification according to this indicator.
4.2.2 In terms of air and water permeability, door blocks are divided into classes given in table 1.
Table 1
About the standard
This measurement is especially useful in areas where your garage door may be exposed to strong winds or if you leave it open for a long time. Since polyurethane adheres to the walls of the door, it doubles the resistance of a door of the same thickness as Styrofoam. Is a 2" thick non-insulated door much less durable than a 1/3 door with PU foam? Do not lie to yourself. It is easy to see why an uninsulated door will be less soundproof than a door of the same thickness that is insulated, especially if it has polyurethane insulation. However, if your garage is connected to your home and you want to block out outside noise, then a polyurethane foam insulated door would be your best bet.
- This is also called tensile strength.
- Yes, at least 122%.
- An uninsulated door is ideal for an unheated garage.
GOST 31173-2003
UDC 692.81-034.14(083.74):006.354
EURASIAN COUNCIL FOR STANDARDIZATION, METROLOGY AND CERTIFICATION (EACC)INTERSTATE STANDARDSTEEL DOOR BLOCKSSpecificationsSteel doorsSpecifications
OKS 91.060.50
Introduction date - 2004-03-01
Foreword
The Eurasian Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (EASC) is a regional association of national standardization bodies of the states that are members of the Commonwealth of Independent States. In the future, national standardization bodies of other states may join the EASC. The Interstate Scientific and Technical Commission for Standardization operates under the EASC, technical regulation and certification in construction (MNTCS), which has been granted the right to adopt interstate standards in the field of construction. 96 “The system of interstate regulatory documents in construction. Basic Provisions»
The main characteristics of metal doors
Metal doors for the entrances of blocks and cooperatives are produced according to the project of the client or our project in accordance with your wishes. The factors that determine the cost of entrance doors are the materials used, the overlay and the mechanisms for them. Metal entrance doors, only visible from the outside and from a distance, or images, look the same, but this is not the case from the materials, mechanisms and security of the locks. Here we can mention the innovations in metal front doors for entrances, namely the access systems that we install for them.
About the standard
1 DEVELOPED by the Center for Certification of Window and Door Equipment and the Federal State Unitary Enterprise Central Design and Technology Bureau (FSUE TsPKTB of the Gosstroy of Russia) with the participation of the Academy of Security and Law and Abloy Oy, the Bjerkboda plant, Finland2 INTRODUCED by the Gosstroy of Russia3 ACCEPTED Interstate Scientific and Technical Commission for Standardization, Technical Regulation and Certification in Construction (MNTKS) May 14, 2003
awesome electronic lock for entrance doors, which guarantees high security and convenience for residents. The electronic lock is a control panel, and the chip and card reader are installed on the front door. When an electronic lock is installed when installing new metal front doors, this is best because the necessary cables are hidden in metal structure. To our offers for metal entrance doors we have added electronic chip lock as additional option.
A similar front door for the block can also be made of sheet metal- one side with ribs inside, no insulating wool, no glazing, no coloring and with ordinary glass, but for less money. If you are wondering how much a front door will cost for your unit, we need to make your suggestion: The size of your current front door. Required quantity mailboxes.
An amazing electronic lock for entrance doors, which guarantees high security and convenience for residents. The electronic lock is a control panel, and the chip and card reader are installed on the front door. When an electronic lock is installed when installing new metal front doors, this is best because the necessary cables are hidden in the metal structure. We have added an electronic chip lock to our offer for metal entrance doors as an additional option.
4 INTRODUCED FOR THE FIRST TIME5 Entered into force on March 1, 2004 as the state standard of the Russian Federation by the Decree of the Gosstroy of Russia dated June 20, 2003 No. 76 indexes of national (state) standards published in these states. Information about changes to this standard is published in the index (catalog) "Interstate standards", and the text of the changes - in the information indexes "Interstate standards". In case of revision or cancellation of this standard, the relevant information will be published in the information index "Interstate Standards".
1 area of use
This standard applies to steel door blocks with installed locking devices (hereinafter referred to as door blocks or products) for buildings and structures for various purposes. The standard does not apply to special-purpose door blocks in terms of additional requirements for fire safety, explosion and bullet resistance, exposure to aggressive environments and etc., as well as on the door blocks of protective cabins according to the current regulatory documentation. The scope of specific types of products is established depending on the operating conditions in accordance with the current building codes and regulations, taking into account the requirements of this standard. The standard can be applied for certification purposes.
This document uses references to the following standards: GOST 9.032-74 ESZKS. Paint coatings. Groups. Technical requirements and designationsGOST 9.301-86 ESZKS. Metallic and non-metallic inorganic coatings. General requirementsGOST 9.303-84 ESZKS. Metallic and non-metallic inorganic coatings. General requirements for the selection of GOST 9.401-91 ESZKS. Paint coatings. General requirements and accelerated test methods for resistance to climatic factorsGOST 9.402-80 ESZKS. Paint coatings. Preparation of metal surfaces before painting GOST 99-96 Rotary cut veneer. SpecificationsGOST 166-89 Calipers. SpecificationsGOST 380-94 Carbon steel of ordinary quality. MarkiGOST 427-75 Measuring metal rulers. SpecificationsGOST 538-2001 Lock and hardware items. General specificationsGOST 1050-88 Rolled bars calibrated, with a special surface finish from high-quality carbon structural steel. General specificationsGOST 2140-81 Visible defects of wood. Classification, terms and definitions, measurement methods GOST 2977-82 Sliced veneer. SpecificationsGOST 4598-86 Wood fiber boards. SpecificationsGOST 5089-2003 Locks and latches for doors. SpecificationsGOST 5264-80 Manual arc welding. Connections are welded. Main types, structural elements and dimensionsGOST 5632-72 High-alloy steels and corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant alloys. MarkiGOST 7016-82 Products from wood and wood materials. Roughness parameters
surfacesGOST 7502-98 Measuring metal tapes. SpecificationsGOST 8026-92 Calibration rulers. SpecificationsGOST 8242-88 Profiled parts made of wood and wood materials for construction. SpecificationsGOST 8713-79 Submerged arc welding. Connections are welded. Main types, structural elements and dimensionsGOST 9416-83 Building levels. SpecificationsGOST 10354-82 Polyethylene film. SpecificationsGOST 11533-75 Automatic and semi-automatic submerged arc welding. Connections are welded at acute and obtuse angles. Main types, structural elements and dimensionsGOST 11534-75 Manual arc welding. Connections are welded at acute and obtuse angles. Main types, structural elements and dimensionsGOST 14771-76 Gas-shielded arc welding. Connections are welded. Main types, structural elements and dimensionsGOST 15140-78 Paintwork materials. Methods for determining adhesionGOST 21778-81 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Basic provisionsGOST 21779-82 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Technological tolerancesGOST 21780-83 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Accuracy calculationGOST 23118-99 Construction steel structures. General specificationsGOST 23518-79 Arc welding in shielding gases. Connections are welded at acute and obtuse angles. Basic types, structural elements and dimensionsGOST 25347-82 Basic standards of interchangeability. ESDP. Tolerance fields and recommended fitGOST 26433.0-85 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Rules for performing measurements. General provisionsGOST 26433.1-89 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Rules for performing measurements. Prefabricated elementsGOST 26602.1-99 Window and door blocks. Methods for determining the resistance to heat transfer GOST 26602.2-99 Window and door blocks. Methods for determining air and water permeability GOST 26602.3-99 Window and door blocks. Method for determining sound insulation GOST 30778-2001 Gaskets sealing from elastomeric materials for window and door blocks. SpecificationsGOST 30971-2002 Mounting seams of adjoining window blocks to wall openings. General specificationsGOST 30972-2002 Glued wooden blanks and parts for window and door blocks. Specifications
3 Terms and definitions
Terms and definitions used in this standard are given in Annex A.
4 Classification and symbol
4.1 Products are classified according to the following criteria: purpose; design options; type of finish; performance indicators; mechanical characteristics; security properties. 4.1.1 By purpose, door blocks are divided into: entrance to the apartment and others intended for operation inside the building). 4.1.2 According to the design options, door blocks are divided: according to the design of the box: with a closed box; with a U-shaped box;
with a U-shaped box with an additional threshold; by the number of canvases (including non-opening ones), the direction and type of opening: single-floor (left and right opening); double-floor (including with canvases of different widths); with non-opening horizontal or vertical canvases - inserts; with opening inside the room; with opening outward; according to the number of sealing circuits in the porch: with one circuit; with two or more circuits. 4.1.3 By type of finish, door blocks are divided into: natural) and insulation; pasted over with decorative film materials; lined with wood or wood-board materials (including natural or synthetic veneer); finished with glass (mirror) materials; finished with decorative metal cladding; combined (including from other materials). Note - In agreement with the customer, it is allowed to use other types of finishes. 4.2 4.2.1 In terms of reduced heat transfer resistance, door blocks are classified into classes: 1 - with reduced heat transfer resistance of 1.0 m2 × ° C / W and more; 2 - with reduced heat transfer resistance from 0.70 to 0.99 m2 × °C / W; 3 - with reduced heat transfer resistance 0.40 - 0.69 m2 × °C / W. Note - Door blocks with reduced heat transfer resistance less than 0.40 m2 × °C/W are not subject to classification according to this indicator.
4.2.2 In terms of air and water permeability, door blocks are divided into classes given in table 1. Table 1 
Notes1 The indicator of the water resistance limit is for entrance door blocks to buildings and premises from the street.2 Door blocks with an air permeability of more than 27 m3 / (h × m2) are not subject to classification according to this indicator. 4.2.3 According to the sound insulation index Rw, door blocks are divided into classes: 1 - with a reduction in airborne noise of 32 dB or more; 2 - » » » » 26-31 dB; 3 - » » » » 20-25 dB. Note - Door blocks with sound insulation less than 20 dB are not subject to classification according to this indicator.
4.3 Door blocks are classified according to the main mechanical characteristics into strength classes given in table 2. Table 2 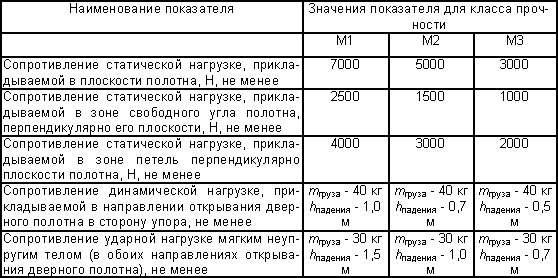
Notes 1 The class of the door unit is set according to the worst result of all types of tests. 2 An example of determining the strength class when testing for resistance to a static load acting perpendicular to the plane of the leaf in the free corner zone is given in Appendix D.
4.4 Subject to availability security properties door blocks are divided into: door blocks of conventional design, equipped with class III-IV locks according to GOST 5089, locking anti-removable devices; door blocks of reinforced design, equipped with class III-IV locks according to GOST 5089, reinforced hinges, blocking anti-removable devices, multi-bar locks with locking along the perimeter, with strength characteristics not lower than class M2; protective door blocks - reinforced door blocks, with strength characteristics not lower than class M1 and meeting the requirements established in Appendix B. , protective design - "Z". 4.5 Structure symbol door blocks: 
Symbol examples: DSV DKN 2100-1270 M3 GOST 31173-2003 - door block internal steel, two-floor, with a closed box, with door leaf opening outwards, standard design, strength class - M3, height 2100 mm, width 1270 mm. outdoor, single-floor right-hand execution, with a threshold, with opening of the leaf inside, class in terms of reduced resistance to heat transfer - 1, class in terms of air and water permeability - 2, class in terms of sound insulation - 2, strength class - M2, reinforced version, height 2300 mm, width 900 mm. When placing an order for manufacturing (delivery) and a passport, it is recommended to indicate: constructive solution, including a description of the filling of the door leaf; a drawing indicating the scheme for opening the canvases and the design of the door block; type and brand of door devices and class of locks; type of finish, box width and other requirements as agreed between the manufacturer and the customer. For export-import deliveries, it is allowed to use a different structure of the symbol specified in the agreement (contract).
5 Technical requirements
5.1 General provisions and requirements for design 5.1.1 Products must comply with the requirements of this standard and be manufactured according to design and technological documentation approved in the prescribed manner. 5.1.2 Cloths of door blocks are a structure welded from steel sheets and rectangular or bent profiles. It is allowed to use the design of "bent box" type canvases, while steel sheets are recommended to be welded together. In the production of welding work, it is recommended to use welding in a shielding gas environment. Places of welding points are set in working documentation.5.1.3 Corner joints of profiles are recommended to be connected by means of welded joints. Other types of joints are allowed, corresponding to or exceeding the strength of welded ones. Variants of door leafs and examples of door block designs are shown in Figures 1-7. 
1 - upper locking crossbar; 2 - upper link of the main lock; 3 - web frame (welded steel profiles); 4 - places for attaching the internal "hatch"; 5 - valve; 6 - the place of attachment of the upper link; 7 - crossbar of the deadbolt of the lever lock; 8 - latch; 9 - deadbolt of the cylinder lock; 10 - lower link of the main lock; 11 - places for fastening the finish; 12 - internal cavity for filler; 13 - vertical thrust guide; 14 - lower locking crossbar; 15 - mounting "eye"; 16 - threshold; 17 - hole for anti-removable crossbar (pin); 18 - anti-removable passive crossbar (pin); 19 - mounting anchor; 20 - box (frame); 21 - combined lever-cylinder lock; 22 - inner steel sheet; 23 - outer steel sheet; 24 - loop knot;
25 - peephole
Figure 1 - An example of the design of a door block, the leaf of which is welded from two steel sheets and steel profiles, the box (frame) is made of a bent steel profile 
Door leaf with two steel sheets, steel box profiles and honeycomb core
Door leaf with an outer steel sheet and an inner sheet of fiberboard, with profiles of complex cross-section and filling with wood or mineral insulation
Door leaf of "bent box" type, with U-shaped steel profiles and foam filling
Door leaf with steel outer sheet and fiberboard inner sheet, steel angle profiles with timber bars and foam core
Figure 2 - Examples of door leaf designs
![]()
Figure 3 - An example of the design of a door block welded from steel sheets and profiles (with filling the middle profile of the frame and leaf with wood and foam material) 
Figure 4 - An example of the construction of a door block welded from steel sheets and profiles, with natural wood cladding 
Figure 5 - An example of the design of a double-leaf door block with wood or wood-veneer cladding board materials(horizontal section) 
Figure 6 - Examples of door leaf structures welded from two flat steel sheets and steel profiles (a) and a “bent box” door leaf (b) with vertical reinforcing profiles 
Figure 7 - Examples of the design of a door leaf welded from steel profiles, with vertical and horizontal reinforcing profiles and installed locks (a) and a door frame (b)
Boxes (frames) are made from a bent profile with a thickness of at least 1.5 mm or from a rectangular profile with a cross section of at least 40x50 mm. Boxes (frames) and door leafs are made at least according to accuracy grade 15 according to GOST 25347.
5.1.4 It is recommended to use vertical and horizontal reinforcing profiles (multipliers) in door leaf structures. It is recommended to use at least two vertical and horizontal reinforcing profiles. It is allowed to place reinforcing profiles at an angle between vertical ones (inclined profiles). Horizontal reinforcing profiles are recommended to be placed in the loop zone or in the zone of anti-removable devices. Examples of the location of reinforcing profiles in the door leaf are shown in Figure 8. 
Figure 8 - Examples of the location of reinforcing profiles in the door leaf
5.1.5 It is allowed to use instead of the internal one-piece steel sheet joined sheet blanks welded along reinforcing profiles, while the places of welding points are set in the design documentation. It is allowed to use solid fiber boards according to GOST 4598 or other solid sheet materials providing sufficient strength.
5.1.6 For the repair of locks and latches at the place of their installation in inner sheet it is recommended to provide a “hatch” that is fixed on mechanical links. The fastening of the locking devices must be strong and reliable, excluding their spontaneous displacement during operation. It is not recommended to fix the lock by welding (if it is technologically necessary to use welding, the possibility of thermal influence on fusible plastic and other parts of the lock should be taken into account). .5.1.8 It is recommended to install at least two contours of sealing gaskets in the structures of external and entrance door blocks to the apartment (to increase sound insulation and resistance to heat transfer). Gaps in the joints of the gaskets are not allowed. The fit of the gaskets must be tight. Sealing gaskets for external door blocks shall be resistant to climatic and atmospheric influences and tested for durability in testing centers accredited to carry out such tests. 5.1.9 The requirements of this standard apply to door blocks with an area not exceeding 9 m2, while the height of the opening door leafs are recommended no more than 2200 mm, and the width - no more than 1200 mm. The use of non-opening horizontal and vertical door leafs is allowed. The recommended weight of door leafs is no more than 250 kg (calculated indicator). and dimensions exceeding the specified values must be confirmed by the results of laboratory tests or additional strength calculations in accordance with current building codes. Note - Largest dimensions leafs of door blocks of specific types, depending on the weight of the leaf, section modulus of the profiles of the frame of the leaf, the rigidity of the section of the middle part of the leaf (including the outer and inner skins, filling, reinforcing profiles), the location (and types) of hinges and locking devices should be given in the design the manufacturer's documentation.5.1.10 The location and dimensions of the holes for installing locks and other locking devices are set in the design documentation, taking into account the requirements of GOST 5089.5.1.11. It is recommended to protect the places of the holes intended for the bolt entry with special boxes. The boxes are welded into the profile of the box (frame) so that they do not interfere with the normal movement of the deadbolt bolts. It is allowed to make holes for the entry of bolts in the door frame. In this case, the dimensions of the hole should be 2-3 mm larger than the corresponding cross-sectional dimensions of the deadbolt. In the closed position, the deadbolt of the lock must enter into door frame to a depth of at least 22 mm. 5.1.12 In the design of products on the hinge side, it is recommended to provide anti-removable passive crossbars (pins). The pins must be firmly installed in the frame of the door leaf or in the frame by welding, pressing or riveting. It is allowed to use other types of fastening of anti-removable pins that do not reduce their strength properties. The size, number and location of the anti-removable pins are set in the working documentation, while to ensure the greatest protection, it is recommended to install the anti-removable pins in the hinge zone. The size, number and location of the mounting "lugs" are set in the working documentation. It is allowed to use other designs of fasteners that provide the necessary rigidity and strength during the installation of the door block. mineral wool, basalt wool, polystyrene or other materials according to regulatory documentation (ND). Filling is laid tightly, without voids. 5.1.15 Products must be safe to use. Safety conditions for the use of products various designs install in project documentation(e.g. door units on escape routes are recommended to be equipped with anti-panic devices). Products must be designed for operational loads in accordance with current building codes. When designing and manufacturing products, calculation programs or calculation methods for determining the strength characteristics of products should be used. 5.1.16 Polymer and synthetic materials, used to fill and finish door panels, must have a conclusion on sanitary safety, provided for by current legislation and drawn up in the prescribed manner
5.2 Dimensions and requirements for limit deviations holes are set in the technical documentation for their manufacture.5.2.2 Limit deviations nominal overall dimensions products shall not exceed ±3.0 mm.
Table 3In millimeters 
Note - The values of the maximum deviations of the dimensions of the gaps under the overlay are given for closed canvases with installed sealing gaskets. The difference in the lengths of the diagonals of rectangular canvases with an area of 1.5 m2 or less should not exceed 2.0 mm, and with an area of \u200b\u200bover 1.5 m2 - 3.0 mm.
5.2.4 Face drop (sag) in welded corner connections shall not exceed 2.0 mm. mm per 1.0 m of length. Note - The flatness of door panels is controlled by measuring the straightness of their edges and the size of the gaps under the overlay. conditions of manufacture and installation. 5.2.8 The dimensions of the welds must correspond to their working sections established in the technical documentation. Deviations of weld sizes from the specified ones should not exceed the values specified in GOST 5264, GOST 8713, GOST 11533, GOST 11534, GOST 14771, GOST 23518.5.2.9 type bolted connection, are accepted according to GOST 23118.
5.3 Characteristics 
Note - The need to use performance indicators marked with an "*" is established in the design and technical documentation based on the purpose of the door blocks.
5.3.2 It is recommended to set the performance indicators of door blocks for a specific purpose in the design documentation for construction (reconstruction) and confirm the results of tests at test centers accredited for the right to conduct them.
5.3.3 Door blocks, depending on the strength class, must withstand the action of static loads in accordance with the requirements of Table 5. Table 5 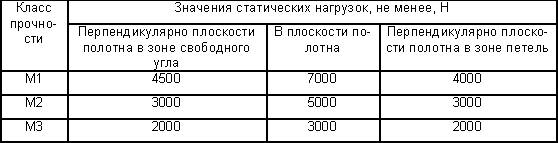
5.3.4 Door blocks, depending on the strength class, must withstand the action of dynamic loads (impact on an obstacle - opening angle limiter, door slope, etc. when opening the leaf) in accordance with the requirements of Table 6. Table 6 
5.3.5 Door units, depending on the strength class, must withstand impact with a soft inelastic body in accordance with the requirements of Table 7. Table 7 
5.3.6 The force applied to the door leaf when closing until the required compression of the sealing gaskets should not exceed 140 N, while in the closed position the latch and the deadbolt of the lock should work without jamming. The force required to open the door leaf must not exceed 100 N (ergonomic requirements). 5.3.7 the material must withstand without destruction the impact of a metal ball weighing 1 kg from a height of 1 m.5.3.8 Appearance products: color, permissible surface defects facing materials and painted elements (risks, scratches, etc.) must correspond to standard samples approved by the head of the manufacturer. Color difference, gloss and surface defects visible to the naked eye from a distance of 0.6 - 0.8 m at natural light not less than 300 lx, not allowed. 5.3.9 Welded joints must be strong and meet the requirements controlled visually: the metal of the weld and the boundary zone must not have cracks. Seam craters at the places where welding stops (ends) must be overcooked (welded); seams must have a smooth or evenly scaly surface without sharp transitions to the base metal; seams must be tight along the entire length and not have burns, narrowing, surfacing, lack of penetration, slag inclusions, etc. 5.3.10 The tensile strength of the metal of the welded joint must not be lower than the requirements for the base metal. The characteristics of the categories and quality level of welded joints are in accordance with GOST 23118.
5.4 Requirements for materials and components (including gaskets) 5.4.1 Materials and components used for the manufacture of door blocks must comply with the requirements of standards, specifications, technical certificates approved in the prescribed manner. 5.4.2 Materials and component parts used for the manufacture of door blocks must be resistant to climatic influences. 5.4.3 The surfaces of steel elements of boxes and leaves must not have cracks, mechanical damage, shells, distortions, rust. On the front surfaces of steel elements, slight local depressions, risks, waviness up to 0.5 mm deep are allowed, which do not reduce the functional properties and quality of products. 5.4.4 Steel parts of structures must be made of steel grades that provide strength characteristics structural elements, welded, bolted and other connections, depending on the nature and conditions of their work. Steel elements are recommended to be made of steel grade not lower than St3kp2 according to GOST 380, rolled sections according to GOST 1050 or high-alloy steel according to GOST 5632.5.4.5 Sealing gaskets should be made of weather-resistant elastic polymer materials in accordance with GOST 30778. The fit of sealing gaskets must be tight, preventing the penetration of water. Sealing gaskets must be installed continuously around the entire perimeter of the porch. 5.4.6 Wooden glued lining panels must meet the requirements of GOST 30972, wooden details— GOST 8242.
5.5 Requirements for hinges, locks and other locking devices 5.5.1 In the manufacture of products, locking and auxiliary devices and hinges are used, specially designed for use in metal door blocks. Examples of designs of hinges and locks are given in Appendix B. The type, number, location and method of fastening of locking devices and hinges are set in the working documentation based on the size and weight of the opening elements of the product, as well as the operating conditions of the door blocks. Cloths of door blocks weighing more than 200 kg, as well as products used in public spaces(schools, hospitals, etc.), it is recommended to hang on three loops. The recommended location of the middle hinge is 150-200 mm lower than the top one. by continuous welding. It is allowed to use other types of fastening of the hinges, which allow to ensure the necessary strength of the structure. and cylinder mechanisms, as well as locks with recoding secret mechanisms. To improve protective properties For door blocks, it is recommended to use multi-bolt locks with locking around the perimeter of the door block or locks with rods with additional locking in the upper and lower horizontal profiles of the frame. To avoid clogging the hole for the lower vertical bolt included in the lower profile of the frame, it is recommended to use deviators. Depending on the purpose of the door blocks in the project documentation, as well as when placing orders, it is necessary to provide for the complete set of products with latches, door closers (closers), opening angle limiters (stops), eyes, chains, etc. 5.5.5 Locking devices must ensure reliable locking opening elements of products. Opening and closing should be easy, smooth, without jamming. - decorative (or protective) coating in accordance with GOST 9.303.5.5.8 In cases where door blocks are installed in public premises (kindergartens, schools, hospitals), it is recommended to use anti-panic devices, smoke detectors and other devices that allow for quick evacuation.5.5. 9 When accepting work, the keys must be handed over to the customer in a sealed package against his signature on receipt.
5.6 Requirements for the finishing of products 5.6.1 The quality of the finish, as well as the requirements for the finishing coating (cladding) can be set by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer in the contract (order) for the manufacture (supply) of products. In this case, it is allowed to evaluate the quality of the finish using reference samples agreed with the customer. 5.6.2 As finishing materials artificial and natural leather, decorative films, MDF boards (with natural or synthetic veneer, smooth or milled), wood, mirrors, plastic, fiberboard, paint and varnish and other materials are used in accordance with the requirements of ND. When choosing facing materials, the operating conditions of the products should be taken into account. Options for finishing door blocks are given in Appendix B.5.6.3 metal surfaces parts before applying paint and polymer coatings must comply with GOST 9.402. Requirements for paint coatings - in accordance with GOST 9.401, designation of coatings - in accordance with GOST 9.032, coating class not lower than IV.5.6.4 The quality of surfaces with a finished paint coating must comply with the requirements established in GOST 9.032. In this case, the first layer should be applied with primer paint, and subsequent layers with protective and decorative paints and varnishes. 5.6.5 The front surfaces of the products should not have cracks, burrs, mechanical damage. The requirements for front surfaces are set in the manufacturer's technical documentation and / or in supply contracts, taking into account GOST 9.301 and GOST 9.032. Non-front surfaces of products may have recesses, risks, waviness and other surface defects that do not reduce the functional properties and quality of products. must have burrs and irregularities. 5.6.6 Color (tone) and degree of gloss (gloss, haze) finishing coating must correspond to standard samples approved by the head of the manufacturer and agreed with the customer. coatings, as well as the procedure for monitoring this indicator, it is recommended to establish in the technical documentation for the manufacture of products. 5.6.9 Protective and protective and decorative coatings must be resistant to temperature and humidity operational influences. types of wood. MDF boards can be finished with sliced veneer according to GOST 2977, peeled veneer according to GOST 99 or synthetic veneer according to ND. It is allowed to use milled or smooth MDF boards. Examples of architectural finishes for door panels MDF boards are given in Appendix B.5.6.11 The front surfaces of wood parts used for finishing door panels should not have processing defects and defects in wood, with the exception of curls, twist, eyes, fiber inclination up to 5% according to GOST 2140. Recommended roughness of front surfaces parts made of wood Rm - no more than 60 microns according to GOST 7016, the moisture content of wood should be in the range from 8 to 12%. 5.6.12 deformations. The shape and dimensions of the sections of the facing profiles adjacent to the steel surfaces of the external products must provide a minimum area of contact with these surfaces, as well as the possibility of ventilating the cavity between them, otherwise the contacting surfaces must be protected by paintwork or other protective materials. 5.6.13 Adhesive materials used when lining door panels with artificial or natural leather, as well as decorative films, must provide sufficient adhesive strength, while not allowed unglued areas, folds, waviness and other defects in appearance.
5.7 Completeness and labeling assembled with locking devices installed. By agreement with the consumer, the set of products may also include closers (closing regulators), opening angle stops and other door devices. The set of keys must be transferred to the customer in a sealed form against the signature of the customer (buyer). 5.7.2 quality (passport) and instructions for the operation of products, including recommendations for installation. 5.7.3 Each product is labeled waterproof marker or a label indicating the name of the manufacturer, the brand of the product, the date of its manufacture and (or) the order number, the sign (stamp) confirming the acceptance of the product by technical control. this product.
6 Acceptance rules
6.1 Products must be accepted by the service technical control manufacturer for compliance with the requirements of this standard, as well as the conditions specified in the contract for the manufacture and supply of products. Confirmation of acceptance of products by the technical control service of the manufacturer is the execution of documents on the acceptance (quality) of products. Products are accepted in batches or individually. When accepting products at the manufacturing plant, a lot is taken as the number of products manufactured within one shift and issued with one quality document. The number of products of the same design, manufactured according to one order, can be taken as the batch volume. 6.2 The product quality requirements established in this standard are confirmed by: incoming control of materials and components; operational production control; acceptance control of finished products; products carried out by the quality control service of the manufacturer; periodic and certification tests of products in independent testing centers; qualification tests.6.3 Procedure for conducting input control and operational production control at the workplace are set in the technological documentation. If the manufacturer completes the door blocks with accessories own production, then they must be accepted and tested in accordance with the requirements of the regulatory documentation for these products.6.4 Acceptance quality control finished products carried out by the method of continuous control. The list of controlled indicators is given in table 8. Finished products that have passed acceptance control are marked. Products that have not passed acceptance control for at least one indicator are rejected. Table 8 
* Type of test I - acceptance tests at acceptance control; test type II - acceptance tests conducted by the quality service of the manufacturer; test type III - periodic tests carried out in independent testing centers. ** Controlled nominal dimensions for test type II are established in the technological documentation.
6.5 Each batch of products undergoes control acceptance tests conducted by the quality service of the manufacturer. The list of controlled indicators and the frequency of control are given in Table 8. For testing, samples of door blocks are taken from a batch of products by random selection in the amount of 3% of the batch volume, but not less than 3 pcs. If there are less than 3 products in a batch, each product is subjected to control. In the event of a negative test result for at least one indicator, at least one sample, a re-check of the quality of products is carried out on a double number of samples according to the indicator that had a negative test result. If a discrepancy is detected again indicator of the established requirements on at least one sample, the control and subsequent batches of products are subjected to continuous control (sorting). If the result of the continuous control is positive, they return to the established procedure for acceptance tests. times in the period specified in table 8, as well as during the certification of products. In justified cases, it is allowed to combine periodic and certification tests. Qualification tests of products are carried out for all indicators when the products are put into production. Tests are carried out at test centers accredited for their right to conduct. Tests to determine the reduced resistance to heat transfer, air permeability, sound insulation are subjected to structures intended for perception of these loads according to their area of application.6.7 The consumer has the right to carry out control check the quality of products, while observing the sampling procedure and test methods specified in this standard. When accepting products by the consumer, a batch considers the number of products shipped for a specific order, but not more than 90 pieces, drawn up with one quality document. 6.8 When accepting products by the consumer it is recommended to use the single-stage quality control plan for products given in Table 9. Table 9 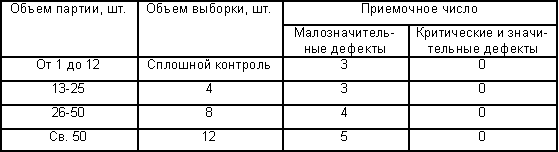
Note - Significant and critical defects include: defects leading to loss performance characteristics, unrecoverable without replacing a part of the product (breakage of a steel profile, etc.), exceeding the maximum deviations of dimensions by more than 1.5 times established in the ND, understaffing of products. Minor defects include removable defects: minor damage to the surface, unadjusted door fixtures and hinges, exceeding the maximum deviations of sizes by less than 1.5 times established in the ND. By agreement of the parties, the acceptance of products by the consumer can be carried out at the manufacturer's warehouse, at the consumer's warehouse or in another place specified in the supply contract. 6.9 Each batch of products must be accompanied by a quality document (passport). An example of filling out a product passport is given in Appendix E.6.10. Acceptance of products by the consumer does not relieve the manufacturer from liability in case of detection of hidden defects that led to a violation of the product performance during the warranty period.
7 Control methods
7.1 Methods for incoming and production operational quality control are established in the technological documentation. 7.2 Methods for quality control of products during acceptance control and acceptance tests 7.2.1 The geometric dimensions of products, as well as the straightness of the edges, are determined using the methods established in GOST 26433.0 and GOST 26433.1. nominal dimensions of product elements, the difference in the lengths of the diagonals and other dimensions are determined using a metal measuring tape according to GOST 7502; using probes according to ND.7.2.2 The maximum deviations from the nominal dimensions of the gaps under the overlay are checked using a set of probes or a ruler in accordance with GOST 427.7.2.3 applied to the upper mating surface, to the lower surface. 7.2.4 The appearance, quality of welds, color and quality of the finish of products are evaluated visually by comparison with standard samples approved in the prescribed manner. Surface defects visible to the naked eye from a distance of 1.5 m in natural light of at least 300 lux are not allowed. sealing gaskets, door appliances, fasteners and other parts, the color and absence of cracks in welded joints, marking and packaging are checked visually. uncompressed gasket. Measurements are made with a caliper or a ruler in accordance with GOST 427. The tightness of sealing gaskets with closed canvases can be determined by the presence of a continuous trace left by a coloring matter (for example, colored chalk), previously applied to the surface of the gaskets and easily removed after inspection. 7.2.7 Work door hinges check by opening ten times - closing the wing elements of the product. In case of detection of deviations in the operation of door devices, they are adjusted and re-checked.
7.3 Methods of control during periodic tests 7.3.1 Reduced resistance to heat transfer is determined according to GOST 26602.1.7.3.2 Air and water permeability is determined according to GOST 26602.2.7.3.3 Sound insulation is determined according to GOST 26602.3.7.3.4 Indicators of reliability, resistance to static, dynamic, impact loads determined according to ND and methods approved in the established manner. When testing for dynamic load resistance, they simulate the load that occurs when the door leaf is suddenly opened (for example, during a draft), at the moment the door leaf contacts the slope of the doorway. Testing for impact resistance with a soft inelastic body is carried out with a three-time blow, for example, with a pear with a lower diameter of (300 ± 5) mm and a mass of (30 ± 0.5) kg, from a fall height according to 5.3.5 into the central zone of the sample. Note - At the end of the test, the door blocks must remain operational , while the deadbolt of the lock and the latch must freely enter their mating parts. Before and after testing the door blocks for failure-free operation, it is recommended to check the fit of the sealing gaskets in accordance with 7.2.6. free angle, to determine the strength class it is recommended to use Use the graph of the dependence of the deflection of the free corner of the web on the applied load, given in Appendix D.7.3.5. Quality control methods for welded joints (5.3.10) are established in the manufacturer's technical documentation in accordance with GOST 5264.
8 Packaging, transport and storage
8.1 Packaging of products must ensure their safety during storage, handling and transportation. 8.2 Devices or parts of devices not installed on products must be packed in polyethylene film according to GOST 10354 or in another packaging material, ensuring their safety, are firmly tied up and delivered complete with products. 8.3 Opening sheets of products must be closed to all locking devices before packaging and transportation. storage and transportation of products, they must be protected from mechanical damage and exposure to atmospheric precipitation. 8.6 When storing and transporting products, it is recommended to install gaskets made of elastic materials between products. 8.7 Products are stored in a vertical or horizontal position on wooden linings, pallets or in special containers indoors.8.8 Guarantee period storage of products - 1 year from the date of shipment of products by the manufacturer.
9 Manufacturer's warranties
9.1 The manufacturer guarantees the compliance of products with the requirements of this standard, provided that the consumer observes the rules for transportation, storage, installation, operation, as well as the scope established in the regulatory and design documentation. 9.2 In agreement with the consumer (customer), the manufacturer provides service maintenance, which includes emergency opening of doors in case of loss or breakage of keys, consultations on the use and operation of door devices and locking mechanisms, repair of products.
Annex A
(mandatory)
Terms and Definitions
In this standard, the following terms are used with their respective definitions. door: An element of a wall structure intended for entry (exit) into interior spaces buildings (structures) or for passage from one room to another and consisting of a doorway, a door block, a system of sealing mounting seams and fasteners and cladding parts. doorway: An opening in the wall intended for mounting a door block and installing a mounting seal. : A structure consisting in the general case of a box (frame) rigidly fixed in doorway, with a leaf hung on hinges with locking devices, which, when the leaf is closed, protects the premises from climatic, noise (and other) influences, as well as unauthorized passage. The door block may include a number of additional elements: door closer, opening angle limiter, peephole, etc. loops).inner sheet: A leaf of the canvas located on the side of the guarded or protected premises or object.profile: The profile part of the box or strapping (frame) of the canvas.recess: The junction (connection node) of the canvas to the profiles of the box.overlap:protrusion of the profile of the canvas ( box), covering the gap in the porch and intended, as a rule, to press the gaskets. Door block of the right (left) opening: Door block with the location of the hinges on the right (left) side when viewed from the opening side of the leaf. or left opening is determined by the location of the leaf, which opens first (figure A.1). 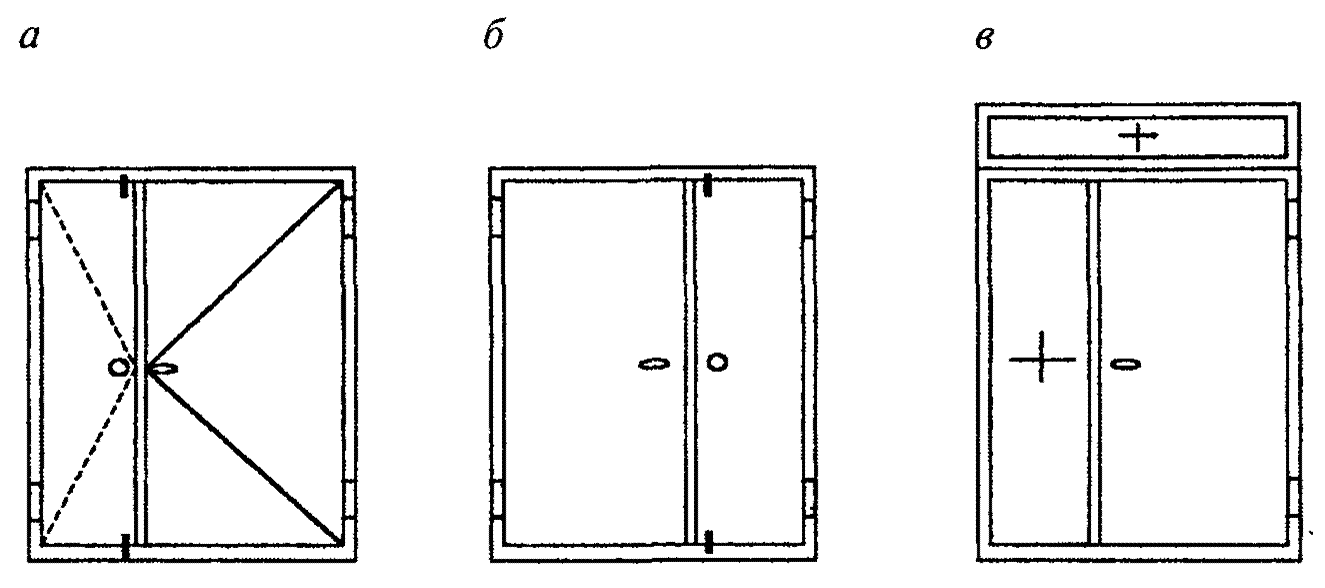
a - right opening door block; b - left opening door block; c - right opening door block with horizontal and vertical leaf inserts
Figure A.1 - Definition of products in the direction of opening of the canvases
horizontal (vertical) leaf-insert: A non-opening leaf installed above or next to the opening leaf (Figure A.1, c). Locking devices: Devices designed to fix door leaves in the closed position (locks, latches, etc.) .reinforcing profile: A profile installed inside the door leaf to provide the necessary rigidity and structural strength. hatch: A metal sheet installed on mechanical links with inside leaf in the place of fastening of the lock, providing the possibility of access to the lock in case of need for its repair. ) and provide additional resistance to burglary of the door block. Mounting "ears": Metal mounting plates, usually welded to the profiles of the box (frame), providing the possibility of fastening the door block in the wall opening.
The characteristics of the door blocks given in Table B.1 are set in the working design documentation and (or) the technical documentation of the manufacturer. Test methods - according to the methods approved in the prescribed manner. Tests are carried out in testing laboratories accredited for the right to conduct such tests.
General requirements for the installation of products
E.1 Requirements for the installation of products are established in the design documentation for construction sites, taking into account the design options adopted in the project for the junction of products to walls, designed for specified climatic and other loads. E.2 Installation of products should be carried out by specialized construction companies or specially trained teams of the enterprise -manufacturer. The ending installation work must be confirmed by an acceptance certificate, which includes the guarantee obligations of the manufacturer of the works. ) typical mounting junctions; a list of materials used (taking into account their compatibility and temperature conditions application); the sequence of technological operations for the installation of door blocks. E.4 When designing and executing the junction nodes, the following conditions must be met: loads outside and operating conditions inside the premises; the design of the junction points of external products (including the location of the door unit along the depth of the opening) should prevent the formation of cold bridges (thermal bridges) that lead to the formation of condensate on internal surfaces doorways; the performance characteristics of the structures of the junction points must meet the requirements established in the building codes. The version of the mounting assembly of the internal door block is shown in Figure E.1.

1 - box (frame) of the door block; 2 - polyurethane foam; 3 - outer seal; 4 - leaf of the door block; 5- inner seal; 6 - decorative frame portal;
7 - casing; 8 - mounting anchor; 9 - mounting ear; 10 - wall
Figure E.1 - Version of the mounting assembly of the internal door unit
E.5 The number and location of the mounting ears, the type, diameter and length of the fasteners are set in the working design documentation, taking into account the material of the walls and the design of the doorway. It is recommended to use building anchors with a diameter of at least 10 mm as fasteners for the installation of products. The distance between the fasteners is at least 700 mm. It is not allowed to use sealants, adhesives, foam insulation, as well as construction nails for fastening products. E.6 Door blocks should be installed in level and plumb. The deviation from the vertical and horizontal profiles of boxes of mounted products should not exceed 1.5 mm per 1 m of length, but not more than 3 mm for the height of the product. In this case, if the opposite profiles are rejected in different sides("twisting" of the box), their total deviation from the normal should not exceed 3 mm. The door block is installed in the prepared doorway symmetrically with respect to the central vertical of the opening. The deviation from symmetry should not exceed 3 mm in the direction of the slope of the opening, intended for fastening the profile of the box with hinges. Deviation from symmetry to the other side of the opening is not recommended. E.7 To fill mounting gaps (seams) of external products, mounting foam, silicone sealants, pre-compressed sealing tapes PSUL (compression tapes), insulating polyurethane foam cords, foam heaters, mineral wool and other materials that have a hygienic conclusion and provide the required performance of the seams. Painting the seams is not recommended. E.8 When arranging assembly seams and installing external door blocks it is recommended to take into account the requirements of GOST 30971.
